Regenerative Medicine
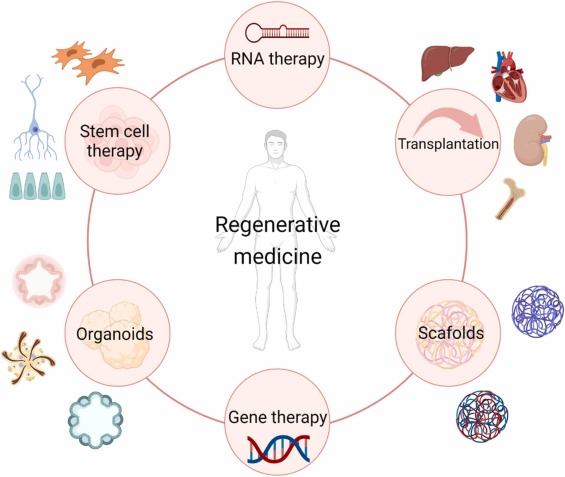
What is Regenerative Medicine?
What Conditions Can Be Treated with Regenerative Medicine?
- Orthopedic injuries (joint pain, tendon and ligament damage, arthritis)
- Neurological disorders (stroke recovery, spinal cord injuries)
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
- Wound healing and burns
- Chronic pain management (back pain, osteoarthritis)
What to Expect During the Procedure?

Your doctor will perform a comprehensive history and physical exam, which may include imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs, to confirm the diagnosis and plan the procedure.

Inform your physician about any medications or supplements you are taking, as certain medications, like blood thinners, may need to be paused before the procedure.

This is not necessary prior to joint injection.

Wear loose, comfortable clothing and arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure.

You will review and sign a consent form and receive detailed guidance on what to expect before, during, and after the procedure.

The area for injection will be thoroughly cleaned with antiseptic solution to prevent injection.

Depending on the procedure the patient's own blood or fat will be collected and processed for injection into affected areas.

Local anesthesia such as Lidocaine will be injected to numb the area (similar to the numbing you would receive at the dentist) to ensure comfort during the procedure.

You get into position depending on the joint being injected


After the Procedure: Post-Care



Benefits of Regenerative Medicine
Minimally Invasive
Enhancing body’s own healing
Faster healing
Pain relief
Lower risk of complications
Improved function and mobility
Risks and Side Effects of Regenerative Medicine
- Mild pain and swelling at the injection site
- Risk of infection (though rare, especially when performed in a sterile environment)
- Allergic reactions (if donor cells or tissues are used)
- Uncertain long-term effects as research is still ongoing in many areas
